Real-World Management Outcomes in Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Objective of study
To evaluate real-world clinical outcomes and management strategies in patients diagnosed with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. The study aims to provide insights into treatment patterns and their effectiveness in routine clinical practice.
This is a multicounty, multicenter, non-interventional, retrospective study
What is HCC?
(Hepatocellular Carcinoma)
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common type of liver cancer, originates from hepatocytes the primary functional cells of the liver. It is closely associated with underlying liver diseases such as cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis infections. Early detection of HCC is crucial, as the disease often progresses silently and can metastasize rapidly, reducing treatment options and survival rates. Globally, the prevalence of HCC varies, with approximately 800,000 new cases diagnosed each year. Despite its severity, awareness about HCC remains low, underscoring the urgent need for widespread screening and timely intervention to improve outcomes
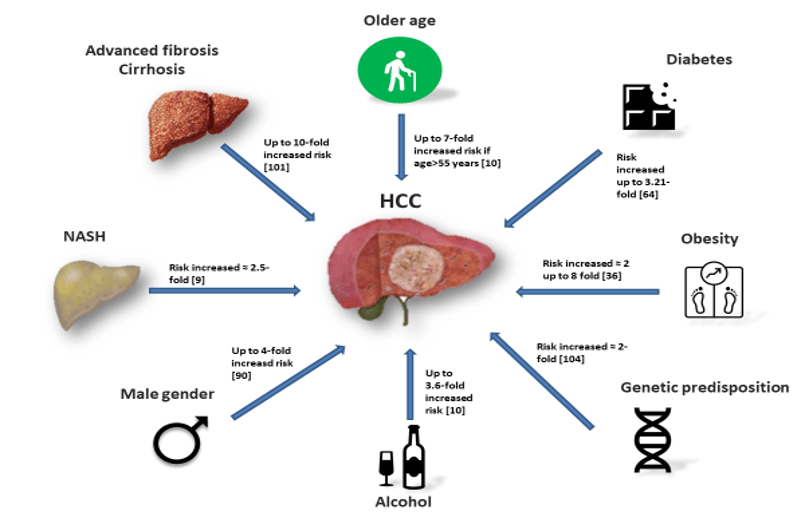
Background of HCC
The exact cause of this condition is not clear, but the
proposed causes include: Chronic infection with certain
hepatitis viruses, DNA mutation of the liver cells
Cirrhosis, Older age, Certain inherited liver disease, Genetic predisposition, Diabetes, Obesity , Exposure to certain chemicals, Excessive alcohol consumption, Gender-Male
Abdominal pain, jaundice, dark urine, reduced appetite, unintended weight loss, nausea & vomiting, abdominal swelling
Blood tests(LFT,CBC , etc.) , Imaging tests(USG,CT Scan,
MRI), Biopsy
Surgery, Ablation, Embolization therapy
Overview of Study
Insights of reports
Study data was summarized and analyzed to get insight into the data.
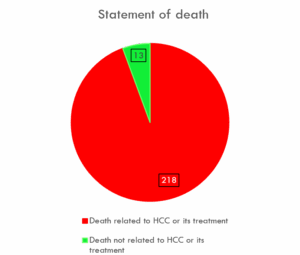 The report aims to determine whether patients experienced death related to HCC or its treatment.
The report aims to determine whether patients experienced death related to HCC or its treatment.
Death related to HCC or its treatment:
218 patients (approximately 21.0% of the study population) experienced death that was either directly related to HCC itself or its treatment.
Death not related to HCC or its treatment:
13 patients (approximately 1.3% of the study population) did not experience death related to HCC or its treatment.
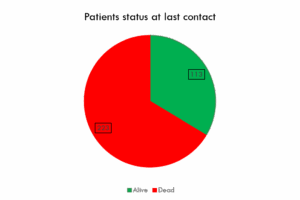 The report assessed the patient’s status at the date of data extraction to determine the current outcome of the study population.
The report assessed the patient’s status at the date of data extraction to determine the current outcome of the study population.
Patients Alive:
There were 113 patients (approximately 10.9% of the study population) who were still alive.
Patients Deceased:
There were 223 patients (approximately 21.5% of the study population) who had passed away
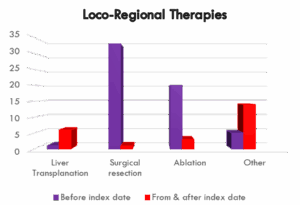 The report analyzed whether patients had a history of loco-regional therapy for HCC, such as liver transplantation, surgical resection, ablation, or other treatments, both before and after the index date
The report analyzed whether patients had a history of loco-regional therapy for HCC, such as liver transplantation, surgical resection, ablation, or other treatments, both before and after the index date
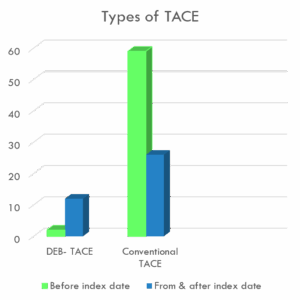 The study aims to analyze the use of Trans Arterial Chemo-Embolization (TACE) in the management of HCC. Specifically, it will determine the proportion of patients who underwent conventional TACE and those who received drug-eluting bead TACE before and after the index date
The study aims to analyze the use of Trans Arterial Chemo-Embolization (TACE) in the management of HCC. Specifically, it will determine the proportion of patients who underwent conventional TACE and those who received drug-eluting bead TACE before and after the index date
- Retrospective Nature
- Limited Treatment Details
- Selection Bias
- Generalizability
- Survivorship Bias
- Data Quality and Completeness

Experienced in delivering more than 200+ studies across multiple therapeutic areas
Summary
By conducting a multicounty, multicenter, non-interventional, and retrospective analysis, the study aimed to describe the diverse treatment approaches and their impact on patient outcomes.
In this study analysis was done on basis of following four factors –
- Summary of Patients Statement of Death
- Summary of Patients Status at Last Contact
- Summary of Patients Treatment History for Loco-Regional Therapy
- Summary of Patients Loco-Regional Therapy
Conclusion
The real-world evidence gathered through this multi-country, multi-center, retrospective study offers valuable insights into the clinical management and outcomes of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). By analyzing patient mortality, survival status, and loco-regional therapy usage, the study underscores the complexity and variation in current treatment strategies. This evidence contributes to a deeper understanding of how therapies such as TACE (Trans Arterial Chemo-Embolization) are utilized in practice and highlights their role in shaping patient outcomes. The findings support more informed clinical decision-making, encourage the adoption of patient-centric care models, and offer
guidance for policymakers developing future treatment guidelines. Ultimately, the study strengthens the knowledge base required to enhance management outcomes and paves the way for further research in improving care for HCC patients globally
Experience of delivering More than
200+ Studies
Under different therapeutic area
Team of experience Professionals
40+ programmers
With an average of 10+ years of experience
Building a joyful client relationship
10+ satisfied clients
Through a commitment to quality and trust.


